Analytic Metrics 101 Part 3: Traffic
Direct, organic, and social, oh my! Traffic is one of those metrics that seems simple enough, but what does it really mean? There are so many ways to read and understand traffic, and we’re here to the rescue.
Before we get started on Part 3 of our series, you’ll notice in Analytics 101 and Acronyms in AdWords, we gave you the answer to “Where Can I Find This Metric?” right after each metric type. However, since we are focused on all Traffic in this article, all the metrics in this article can be found here: select ACQUISITION in the left navigation tab, then select Overview. By scrolling down on that same page, you can see more detail, click on the traffic type, and learn more about how people found your site.
User/Visitor
Definition: Users/Visitors that visit your site. The initial session by a user during any given date range is considered to be an additional visit and an additional visitor. Any future sessions from the same user during the selected time period are counted as additional visits, but not as additional visitors.
Translation: The terms Users and Visitors are used interchangeably and mean exactly the same thing. Essentially, anyone who visits your website (during your selected date range) counts as a User, no matter how many times they visited your website during that time. That means that the User/Visitor metric will always be smaller than Pageviews.
Where Can I Find This Metric: You’ll see User/Visitor all over Google Analytics, but most prominently under the Overview section in the AUDIENCE and ACQUISITION tabs along the left side navigation.
Traffic
Definition: The number of visitors to a website, and the pages they click on, is called website traffic.
Translation: Traffic is the overarching term we use to describe Users/Visitors and their activity on your site. There are different types of traffic: Direct, Organic, Referral, Social, Email, Display and Paid. These describe exactly how that traffic arrived at your site.
Where Can I Find This Metric: There isn’t one place where Traffic is written out, but all of the terms below impact total traffic. Find a summary of your traffic by selecting ACQUISITION in the left navigation tab, then select Overview.
Direct Traffic
Definition: Visitors who visited the site by typing the URL directly into their browser. ‘Direct’ can also refer to the visitors who clicked on the links from their bookmarks/favorites, untagged links within emails, or links from documents that don’t include tracking variables (such as PDFs or Word documents).
Translation: We all have our favorite websites, right? From shopping to entertainment, there are certain sites that we just know exactly how to get to: type the URL right into the search bar. Specific examples could be “mediag.com” or “amazon.com”.

Organic Traffic
Definition: Visitors referred by an unpaid search engine listing, e.g. a Google.com search.
Translation: When visitors start their search off by going to a search engine like Google or Bing and search a phrase like “auto repair shop”, thousands of results show up. Sometimes you’ll notice that the first couple of results you see are ads, which are Paid Listings, and if you click these it is Paid Traffic. However, most of the results after that are organic results, and when you click on those results, that is considered organic traffic.
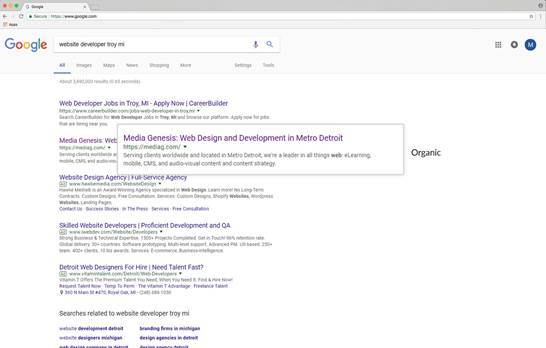
Referral Traffic
Definition: Visitors referred by links on other websites.
Translation: Have you ever been talking to a friend who referred you to go to a different salon, grocery store, or restaurant? Referral Traffic is kind of like that. You’ve probably noticed that most blog or news articles link to another blog, news, or reference article on a related topic. When any website has a link/page of content that links to any other websites’ page, the second page is getting a traffic referral from the first page, hence the name. Linking to and having your website’s pages linked on other credible websites can help boost your SEO ranking.
Social Traffic
Definition: Visitors referred by links on Social Media websites.
Translation: Social Traffic is pretty similar to Referral traffic, except it’s coming in from a link on social media, like Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Instagram, etc. It’s important to know that whether or not your organization is running ads on social media, all the traffic (“organic” social media and “paid” social media) will be lumped into this metric. If you want to track traffic from specific social campaigns, we can help you build custom tracking links. We can also set up alerts or other methods of filtering social media paid versus organic traffic for you.
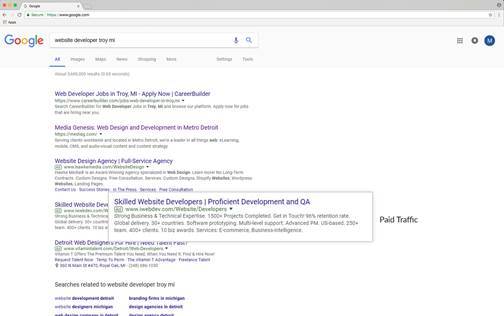
Paid Traffic
Definition: Paid Traffic is a way of sending visitors to your website using search engine marketing.
Translation: This one is pretty self-explanatory. Whenever you are paying for someone to get to your website, that is Paid Traffic. Paid Traffic should be treated like any other marketing tactic: with a strategic approach that lines up with your business’ goals.
Not sure if Paid Traffic solutions are right for you? Want to learn more about analyzing your websites metrics and getting better quality traffic? Check out the other two parts of our three-part series for more information: Analytics 101 and Acronyms in AdWords. Give us a call at 248-687-7888 or reach out on Facebook or Twitter (@MediaG) to work with us on Search Engine Advertising or website Analytics.


.png)
